import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.font_manager as font_manager
from IPython.core.display import HTML
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from directory_tree import display_treeOptimal Plot Sizes for Scientific Works
In this guide, I will show you how to create plots in a standardized, publication-ready size. These tips are suitable for both Jupyter notebooks and scientific works such as term papers.
When exporting plots as PDF files, vector graphics are created that can be scaled losslessly afterward. While this allows flexible adaptation to single or double-column layout formats, it can lead to inconsistencies: different scaling factors often result in varying sizes of axis labels and markers, which impairs the overall appearance of the work.
The better strategy is to use uniform plot sizes from the beginning:
- Define standards for single and double-column figures
- Establish uniform sizes for axis labels and markers
- Create all plots directly in the final size
\[ \frac{\sin(x)}{x}=0 \]
Below, I present practical techniques that allow you to create and save publication-ready plots directly from Jupyter notebooks.
Creating a Diagram with a Specific Bounding Box Size
When creating a plot in matplotlib, you can set a size with the figsize parameter, e.g.
plt.figure(figsize=(3,2))for a figure with a width of 3 inches or 7.62 cm and a height of 2 inches (5.08 cm). If you don’t use this parameter or even don’t use the plt.figure() command, matplotlib uses the default size, which is often 8 inches by 6 inches. This default size is much too large, as the figure would then be almost as wide as a whole A4 page. An appropriate size for a plot in a single column of a two-column document would be the above-mentioned 3 inches by 2 inches, as the total page width of 21 cm minus a margin of about 3 cm on each side results in a column width of approximately (21-6)/2=7.5 cm.
The plot shown in Figure 2 was created with the following commands
plt.figure(figsize=(3,2), dpi=150)
x=np.linspace(0,np.pi*4,200)
plt.plot(x,np.sin(x),color='k')
plt.xlabel(r"angle $\theta$ in [rad]")
plt.ylabel(r"$\sin(\theta)$")
plt.savefig("figure_example.pdf",
bbox_inches = 'tight')
plt.show()The resulting PDF file contains a graphic with a bounding box that is exactly 3 inches by 2 inches. When you insert the diagram into any drawing program like Adobe Illustrator, Affinity Designer, or even into a word processing software like Word or Pages, the bounding box of this diagram has exactly this size, and you can arrange additional diagrams to create a complete figure without having to change the scaling. If you use the diagram in a two-column LaTeX manuscript, it can be used without scaling, i.e., includegraphics{Figure 1.pdf} will display it at the appropriate size across one column.
There are a few more things to note.
While the bounding box of this figure has this size, the axis frame is smaller, and often there is some empty space on the left/bottom side between the axis labels and the edge of the bounding box. This depends heavily on your specific diagram. How to create a figure with a fixed axis frame size is covered in the second section.
The font size on the axis is now 10 or 11 points, which corresponds to the font size of most documents you create with this figure. I used the following plt.rcParams: ‘axes.labelsize’: 11, ‘xtick.labelsize’ : 10, ‘ytick.labelsize’ : 10 for the shown representation.
You will also notice that working with this figure size in a Jupyter notebook is not good. This has to do with how Jupyter translates the output into a PNG file that is displayed inline. One way to enlarge the plot in the Jupyter notebook while maintaining the PDF size is to increase the dpi parameter in the
plt.figure(figsize=(3,2), dpi=150)command. Normally it is set to dpi=75, which is now much too small. A setting of dpi=150 seems to be a reasonable compromise between screen and print size. If you want to be completely independentThe
plt.savefigcommand uses an additionalbbox_inches = 'tight'parameter that ensures that the bounding box really encloses all components of the plot precisely.
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 12,
'lines.linewidth': 1,
'lines.markersize': 10,
'axes.labelsize': 11,
'xtick.labelsize' : 10,
'ytick.labelsize' : 10,
'xtick.top' : True,
'xtick.direction' : 'in',
'ytick.right' : True,
'ytick.direction' : 'in',
'figure.dpi': 150})
#| autorun: false
def get_size(w,h):
return((w/2.54,h/2.54))plt.figure(figsize=get_size(14,6))
x=np.linspace(0,np.pi*4,200)
plt.plot(x,np.sin(x),color='k')
plt.xlabel(r"angle $\theta$ in [rad]")
plt.ylabel(r"$\sin(\theta)$")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("figure_example3.pdf", transparent=True)
plt.show()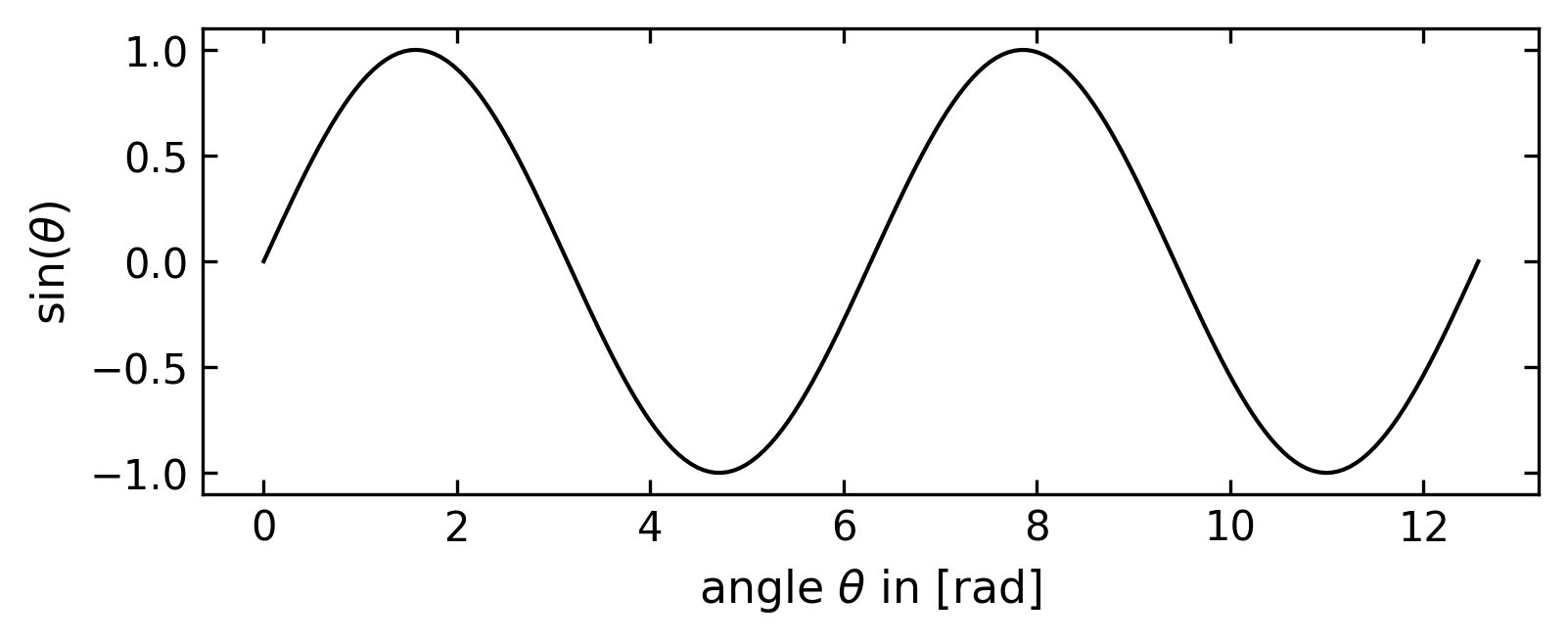
When you load this image into any software, you get an image with a size that corresponds to the set width.
Creating a Diagram with a Specific Axis Frame Size
The axis frame is the box of the frame that provides the axes. When creating a figure with the plt.figure() command, the axis frame is calculated by matplotlib to fit within the bounding box specified by figsize, so that all axis labels also fit inside. The axis frame is therefore smaller than the specified bounding box and often depends on the axis labels and other things. If you want to create a plot with a fixed size of the axis frame, it makes sense to include a function in your code that sets the size of the axis frame. This function could be
def set_size(w,h, ax=None):
""" w, h: width, height in inches """
if not ax: ax=plt.gca()
l = ax.figure.subplotpars.left
r = ax.figure.subplotpars.right
t = ax.figure.subplotpars.top
b = ax.figure.subplotpars.bottom
figw = float(w)/(r-l)
figh = float(h)/(t-b)
ax.figure.set_size_inches(figw, figh)where you need to specify the desired width and height (in inches) of the current axis ax. The function doesn’t return anything but directly sets the size.
def set_size(w,h, ax=None):
""" w, h: width, height in inches """
if not ax: ax=plt.gca()
l = ax.figure.subplotpars.left
r = ax.figure.subplotpars.right
t = ax.figure.subplotpars.top
b = ax.figure.subplotpars.bottom
figw = float(w)/(r-l)
figh = float(h)/(t-b)
ax.figure.set_size_inches(figw, figh)
fig=plt.figure(dpi=150)
ax=plt.axes()
ax.plot(x,np.sin(x),color='k')
ax.set_xlabel(r"angle $\theta$ in [rad]")
ax.set_ylabel(r"$\sin(\theta)$")
set_size(3,2)
plt.savefig("figure_example2.pdf", bbox_inches='tight', transparent=True)
plt.show()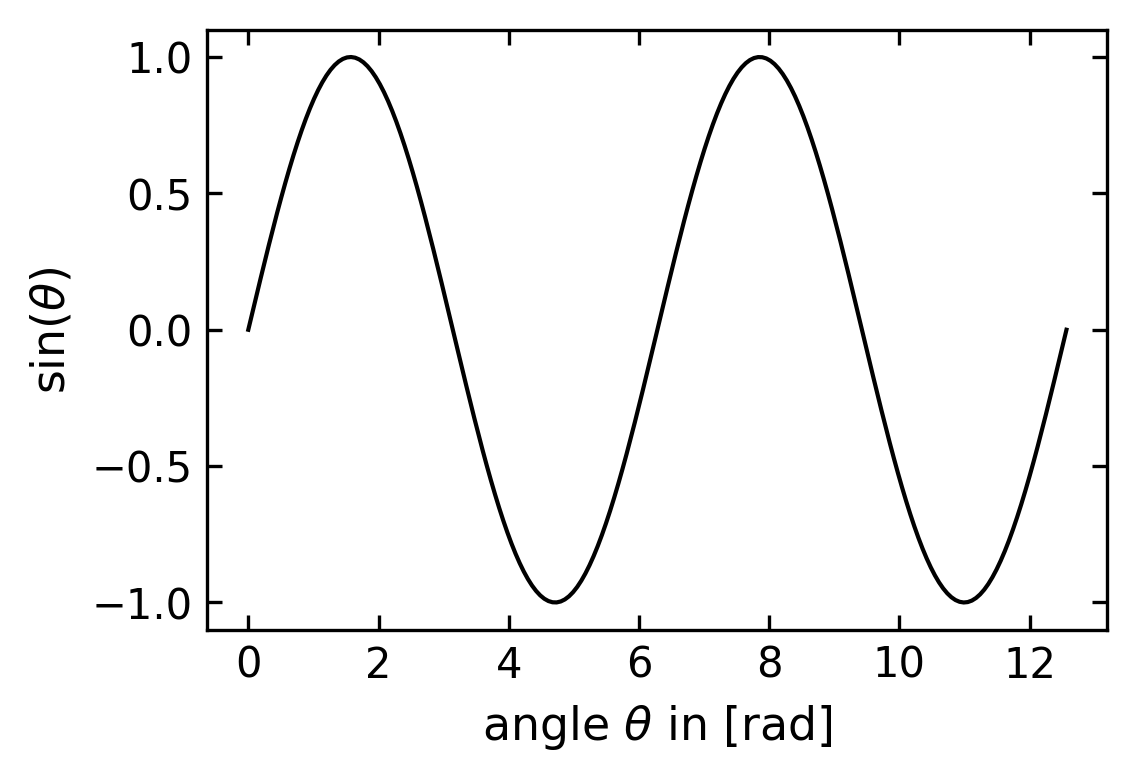
When you load this figure into a graphics program or word processing software, the figure field should have a size of 7.62 cm by 5.08 cm, without any rescaling:
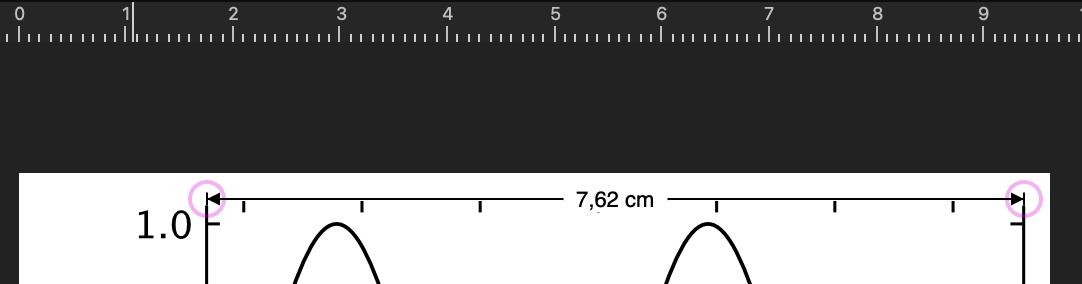
Selecting Fonts
Matplotlib can access a range of different fonts. It can be difficult to find the right font for the formula style of your document or publication. A list of fonts available to Matplotlib can be retrieved with the following code snippet, which I found here.
from IPython.display import HTML, display
def make_html(fontname):
return "<p>{font}: <span style='font-family:{font}; font-size: 24px;'>{font}</p>".format(font=fontname)
code = "\n".join([make_html(font) for font in sorted(set([f.name for f in font_manager.fontManager.ttflist]))])
display(HTML("<div style='column-count: 2;'>{}</div>".format(code))).Aqua Kana: .Aqua Kana
.CJK Symbols Fallback HK: .CJK Symbols Fallback HK
.Keyboard: .Keyboard
.New York: .New York
.SF Arabic: .SF Arabic
.SF Arabic Rounded: .SF Arabic Rounded
.SF Armenian: .SF Armenian
.SF Armenian Rounded: .SF Armenian Rounded
.SF Camera: .SF Camera
.SF Compact Rounded: .SF Compact Rounded
.SF Georgian: .SF Georgian
.SF Georgian Rounded: .SF Georgian Rounded
.SF Hebrew: .SF Hebrew
.SF Hebrew Rounded: .SF Hebrew Rounded
.SF NS Mono: .SF NS Mono
.SF NS Rounded: .SF NS Rounded
.SF Soft Numeric: .SF Soft Numeric
.ThonburiUI: .ThonburiUI
Academy Engraved LET: Academy Engraved LET
Adelle Sans Devanagari: Adelle Sans Devanagari
AkayaKanadaka: AkayaKanadaka
AkayaTelivigala: AkayaTelivigala
Al Bayan: Al Bayan
Al Nile: Al Nile
Al Tarikh: Al Tarikh
American Typewriter: American Typewriter
Andale Mono: Andale Mono
Annai MN: Annai MN
Apple Braille: Apple Braille
Apple Chancery: Apple Chancery
Apple LiGothic: Apple LiGothic
Apple LiSung: Apple LiSung
Apple SD Gothic Neo: Apple SD Gothic Neo
Apple Symbols: Apple Symbols
AppleGothic: AppleGothic
AppleMyungjo: AppleMyungjo
Arial: Arial
Arial Black: Arial Black
Arial Hebrew: Arial Hebrew
Arial Narrow: Arial Narrow
Arial Rounded MT Bold: Arial Rounded MT Bold
Arial Unicode MS: Arial Unicode MS
Arima Koshi: Arima Koshi
Arima Madurai: Arima Madurai
Athelas: Athelas
Avenir: Avenir
Avenir Next: Avenir Next
Avenir Next Condensed: Avenir Next Condensed
Ayuthaya: Ayuthaya
BM Dohyeon: BM Dohyeon
BM Hanna 11yrs Old: BM Hanna 11yrs Old
BM Hanna Air: BM Hanna Air
BM Hanna Pro: BM Hanna Pro
BM Jua: BM Jua
BM Kirang Haerang: BM Kirang Haerang
BM Yeonsung: BM Yeonsung
Baghdad: Baghdad
Bai Jamjuree: Bai Jamjuree
Baloo 2: Baloo 2
Baloo Bhai 2: Baloo Bhai 2
Baloo Bhaijaan: Baloo Bhaijaan
Baloo Bhaina 2: Baloo Bhaina 2
Baloo Chettan 2: Baloo Chettan 2
Baloo Da 2: Baloo Da 2
Baloo Paaji 2: Baloo Paaji 2
Baloo Tamma 2: Baloo Tamma 2
Baloo Tammudu 2: Baloo Tammudu 2
Baloo Thambi 2: Baloo Thambi 2
Bangla MN: Bangla MN
Bangla Sangam MN: Bangla Sangam MN
Baoli SC: Baoli SC
Baskerville: Baskerville
Beirut: Beirut
BiauKaiHK: BiauKaiHK
Big Caslon: Big Caslon
Bodoni 72: Bodoni 72
Bodoni 72 Oldstyle: Bodoni 72 Oldstyle
Bodoni 72 Smallcaps: Bodoni 72 Smallcaps
Bodoni Ornaments: Bodoni Ornaments
Bradley Hand: Bradley Hand
Brush Script MT: Brush Script MT
Cambay Devanagari: Cambay Devanagari
Chakra Petch: Chakra Petch
Chalkboard: Chalkboard
Chalkboard SE: Chalkboard SE
Chalkduster: Chalkduster
Charm: Charm
Charmonman: Charmonman
Charter: Charter
Cochin: Cochin
Comic Sans MS: Comic Sans MS
Copperplate: Copperplate
Corsiva Hebrew: Corsiva Hebrew
Courier: Courier
Courier New: Courier New
DIN Alternate: DIN Alternate
DIN Condensed: DIN Condensed
Damascus: Damascus
DecoType Naskh: DecoType Naskh
DejaVu Sans: DejaVu Sans
DejaVu Sans Display: DejaVu Sans Display
DejaVu Sans Mono: DejaVu Sans Mono
DejaVu Serif: DejaVu Serif
DejaVu Serif Display: DejaVu Serif Display
Devanagari MT: Devanagari MT
Devanagari Sangam MN: Devanagari Sangam MN
Didot: Didot
Diwan Kufi: Diwan Kufi
Diwan Thuluth: Diwan Thuluth
Euphemia UCAS: Euphemia UCAS
Fahkwang: Fahkwang
Farah: Farah
Farisi: Farisi
Futura: Futura
Galvji: Galvji
Geeza Pro: Geeza Pro
Geneva: Geneva
Georgia: Georgia
Gill Sans: Gill Sans
Gotu: Gotu
Gujarati MT: Gujarati MT
Gujarati Sangam MN: Gujarati Sangam MN
GungSeo: GungSeo
Gurmukhi MN: Gurmukhi MN
Gurmukhi MT: Gurmukhi MT
Gurmukhi Sangam MN: Gurmukhi Sangam MN
Hannotate SC: Hannotate SC
HanziPen SC: HanziPen SC
HeadLineA: HeadLineA
Hei: Hei
Heiti TC: Heiti TC
Helvetica: Helvetica
Helvetica Neue: Helvetica Neue
Herculanum: Herculanum
Hiragino Maru Gothic Pro: Hiragino Maru Gothic Pro
Hiragino Mincho ProN: Hiragino Mincho ProN
Hiragino Sans: Hiragino Sans
Hiragino Sans GB: Hiragino Sans GB
Hiragino Sans TC: Hiragino Sans TC
Hoefler Text: Hoefler Text
Hubballi: Hubballi
ITF Devanagari: ITF Devanagari
Impact: Impact
InaiMathi: InaiMathi
Iowan Old Style: Iowan Old Style
Jaini: Jaini
Jaini Purva: Jaini Purva
K2D: K2D
Kai: Kai
Kailasa: Kailasa
Kaiti SC: Kaiti SC
Kannada MN: Kannada MN
Kannada Sangam MN: Kannada Sangam MN
Katari: Katari
Kavivanar: Kavivanar
Kefa: Kefa
Khmer MN: Khmer MN
Khmer Sangam MN: Khmer Sangam MN
Klee: Klee
KoHo: KoHo
Kodchasan: Kodchasan
Kohinoor Bangla: Kohinoor Bangla
Kohinoor Devanagari: Kohinoor Devanagari
Kohinoor Gujarati: Kohinoor Gujarati
Kohinoor Telugu: Kohinoor Telugu
Kokonor: Kokonor
Krub: Krub
Krungthep: Krungthep
KufiStandardGK: KufiStandardGK
Lahore Gurmukhi: Lahore Gurmukhi
Lantinghei SC: Lantinghei SC
Lao MN: Lao MN
Lao Sangam MN: Lao Sangam MN
Lava Devanagari: Lava Devanagari
Lava Kannada: Lava Kannada
Lava Telugu: Lava Telugu
LiHei Pro: LiHei Pro
LiSong Pro: LiSong Pro
Libian SC: Libian SC
LingWai SC: LingWai SC
LingWai TC: LingWai TC
Lucida Grande: Lucida Grande
Luminari: Luminari
Maku: Maku
Malayalam MN: Malayalam MN
Malayalam Sangam MN: Malayalam Sangam MN
Mali: Mali
Marion: Marion
Marker Felt: Marker Felt
Menlo: Menlo
Microsoft Sans Serif: Microsoft Sans Serif
Mishafi: Mishafi
Mishafi Gold: Mishafi Gold
Modak: Modak
Monaco: Monaco
Mshtakan: Mshtakan
Mukta: Mukta
Mukta Mahee: Mukta Mahee
Mukta Malar: Mukta Malar
Mukta Vaani: Mukta Vaani
Muna: Muna
Myanmar MN: Myanmar MN
Myanmar Sangam MN: Myanmar Sangam MN
Nadeem: Nadeem
Nanum Brush Script: Nanum Brush Script
Nanum Gothic: Nanum Gothic
Nanum Myeongjo: Nanum Myeongjo
New Peninim MT: New Peninim MT
Niramit: Niramit
Noteworthy: Noteworthy
Noto Nastaliq Urdu: Noto Nastaliq Urdu
Noto Sans Adlam: Noto Sans Adlam
Noto Sans Armenian: Noto Sans Armenian
Noto Sans Avestan: Noto Sans Avestan
Noto Sans Bamum: Noto Sans Bamum
Noto Sans Bassa Vah: Noto Sans Bassa Vah
Noto Sans Batak: Noto Sans Batak
Noto Sans Bhaiksuki: Noto Sans Bhaiksuki
Noto Sans Brahmi: Noto Sans Brahmi
Noto Sans Buginese: Noto Sans Buginese
Noto Sans Buhid: Noto Sans Buhid
Noto Sans Canadian Aboriginal: Noto Sans Canadian Aboriginal
Noto Sans Carian: Noto Sans Carian
Noto Sans Caucasian Albanian: Noto Sans Caucasian Albanian
Noto Sans Chakma: Noto Sans Chakma
Noto Sans Cham: Noto Sans Cham
Noto Sans Coptic: Noto Sans Coptic
Noto Sans Cuneiform: Noto Sans Cuneiform
Noto Sans Cypriot: Noto Sans Cypriot
Noto Sans Duployan: Noto Sans Duployan
Noto Sans Egyptian Hieroglyphs: Noto Sans Egyptian Hieroglyphs
Noto Sans Elbasan: Noto Sans Elbasan
Noto Sans Glagolitic: Noto Sans Glagolitic
Noto Sans Gothic: Noto Sans Gothic
Noto Sans Gunjala Gondi: Noto Sans Gunjala Gondi
Noto Sans Hanifi Rohingya: Noto Sans Hanifi Rohingya
Noto Sans Hanunoo: Noto Sans Hanunoo
Noto Sans Hatran: Noto Sans Hatran
Noto Sans Imperial Aramaic: Noto Sans Imperial Aramaic
Noto Sans Inscriptional Pahlavi: Noto Sans Inscriptional Pahlavi
Noto Sans Inscriptional Parthian: Noto Sans Inscriptional Parthian
Noto Sans Javanese: Noto Sans Javanese
Noto Sans Kaithi: Noto Sans Kaithi
Noto Sans Kannada: Noto Sans Kannada
Noto Sans Kayah Li: Noto Sans Kayah Li
Noto Sans Kharoshthi: Noto Sans Kharoshthi
Noto Sans Khojki: Noto Sans Khojki
Noto Sans Khudawadi: Noto Sans Khudawadi
Noto Sans Lepcha: Noto Sans Lepcha
Noto Sans Limbu: Noto Sans Limbu
Noto Sans Linear A: Noto Sans Linear A
Noto Sans Linear B: Noto Sans Linear B
Noto Sans Lisu: Noto Sans Lisu
Noto Sans Lycian: Noto Sans Lycian
Noto Sans Lydian: Noto Sans Lydian
Noto Sans Mahajani: Noto Sans Mahajani
Noto Sans Mandaic: Noto Sans Mandaic
Noto Sans Manichaean: Noto Sans Manichaean
Noto Sans Marchen: Noto Sans Marchen
Noto Sans Masaram Gondi: Noto Sans Masaram Gondi
Noto Sans Meetei Mayek: Noto Sans Meetei Mayek
Noto Sans Mende Kikakui: Noto Sans Mende Kikakui
Noto Sans Meroitic: Noto Sans Meroitic
Noto Sans Miao: Noto Sans Miao
Noto Sans Modi: Noto Sans Modi
Noto Sans Mongolian: Noto Sans Mongolian
Noto Sans Mro: Noto Sans Mro
Noto Sans Multani: Noto Sans Multani
Noto Sans Myanmar: Noto Sans Myanmar
Noto Sans NKo: Noto Sans NKo
Noto Sans Nabataean: Noto Sans Nabataean
Noto Sans New Tai Lue: Noto Sans New Tai Lue
Noto Sans Newa: Noto Sans Newa
Noto Sans Ol Chiki: Noto Sans Ol Chiki
Noto Sans Old Hungarian: Noto Sans Old Hungarian
Noto Sans Old Italic: Noto Sans Old Italic
Noto Sans Old North Arabian: Noto Sans Old North Arabian
Noto Sans Old Permic: Noto Sans Old Permic
Noto Sans Old Persian: Noto Sans Old Persian
Noto Sans Old South Arabian: Noto Sans Old South Arabian
Noto Sans Old Turkic: Noto Sans Old Turkic
Noto Sans Oriya: Noto Sans Oriya
Noto Sans Osage: Noto Sans Osage
Noto Sans Osmanya: Noto Sans Osmanya
Noto Sans Pahawh Hmong: Noto Sans Pahawh Hmong
Noto Sans Palmyrene: Noto Sans Palmyrene
Noto Sans Pau Cin Hau: Noto Sans Pau Cin Hau
Noto Sans PhagsPa: Noto Sans PhagsPa
Noto Sans Phoenician: Noto Sans Phoenician
Noto Sans Psalter Pahlavi: Noto Sans Psalter Pahlavi
Noto Sans Rejang: Noto Sans Rejang
Noto Sans Samaritan: Noto Sans Samaritan
Noto Sans Saurashtra: Noto Sans Saurashtra
Noto Sans Sharada: Noto Sans Sharada
Noto Sans Siddham: Noto Sans Siddham
Noto Sans Sora Sompeng: Noto Sans Sora Sompeng
Noto Sans Sundanese: Noto Sans Sundanese
Noto Sans Syloti Nagri: Noto Sans Syloti Nagri
Noto Sans Syriac: Noto Sans Syriac
Noto Sans Tagalog: Noto Sans Tagalog
Noto Sans Tagbanwa: Noto Sans Tagbanwa
Noto Sans Tai Le: Noto Sans Tai Le
Noto Sans Tai Tham: Noto Sans Tai Tham
Noto Sans Tai Viet: Noto Sans Tai Viet
Noto Sans Takri: Noto Sans Takri
Noto Sans Thaana: Noto Sans Thaana
Noto Sans Tifinagh: Noto Sans Tifinagh
Noto Sans Tirhuta: Noto Sans Tirhuta
Noto Sans Ugaritic: Noto Sans Ugaritic
Noto Sans Vai: Noto Sans Vai
Noto Sans Wancho: Noto Sans Wancho
Noto Sans Warang Citi: Noto Sans Warang Citi
Noto Sans Yi: Noto Sans Yi
Noto Serif Ahom: Noto Serif Ahom
Noto Serif Balinese: Noto Serif Balinese
Noto Serif Hmong Nyiakeng: Noto Serif Hmong Nyiakeng
Noto Serif Kannada: Noto Serif Kannada
Noto Serif Myanmar: Noto Serif Myanmar
Noto Serif Yezidi: Noto Serif Yezidi
October Compressed Devanagari: October Compressed Devanagari
October Compressed Tamil: October Compressed Tamil
October Condensed Devanagari: October Condensed Devanagari
October Condensed Tamil: October Condensed Tamil
October Devanagari: October Devanagari
October Tamil: October Tamil
Optima: Optima
Oriya MN: Oriya MN
Oriya Sangam MN: Oriya Sangam MN
Osaka: Osaka
PCMyungjo: PCMyungjo
PSL Ornanong Pro: PSL Ornanong Pro
PT Mono: PT Mono
PT Sans: PT Sans
PT Serif: PT Serif
PT Serif Caption: PT Serif Caption
Padyakke Expanded One: Padyakke Expanded One
Palatino: Palatino
Papyrus: Papyrus
Party LET: Party LET
Phosphate: Phosphate
PilGi: PilGi
Plantagenet Cherokee: Plantagenet Cherokee
Raanana: Raanana
Rockwell: Rockwell
STFangsong: STFangsong
STHeiti: STHeiti
STIX Two Math: STIX Two Math
STIX Two Text: STIX Two Text
STIXGeneral: STIXGeneral
STIXIntegralsD: STIXIntegralsD
STIXIntegralsSm: STIXIntegralsSm
STIXIntegralsUp: STIXIntegralsUp
STIXIntegralsUpD: STIXIntegralsUpD
STIXIntegralsUpSm: STIXIntegralsUpSm
STIXNonUnicode: STIXNonUnicode
STIXSizeFiveSym: STIXSizeFiveSym
STIXSizeFourSym: STIXSizeFourSym
STIXSizeOneSym: STIXSizeOneSym
STIXSizeThreeSym: STIXSizeThreeSym
STIXSizeTwoSym: STIXSizeTwoSym
STIXVariants: STIXVariants
Sama Devanagari: Sama Devanagari
Sama Gujarati: Sama Gujarati
Sama Gurmukhi: Sama Gurmukhi
Sama Kannada: Sama Kannada
Sama Malayalam: Sama Malayalam
Sama Tamil: Sama Tamil
Sana: Sana
Sarabun: Sarabun
Sathu: Sathu
Savoye LET: Savoye LET
Seravek: Seravek
Shobhika: Shobhika
Shree Devanagari 714: Shree Devanagari 714
SignPainter: SignPainter
Silom: Silom
SimSong: SimSong
Sinhala MN: Sinhala MN
Sinhala Sangam MN: Sinhala Sangam MN
Skia: Skia
Snell Roundhand: Snell Roundhand
Songti SC: Songti SC
Srisakdi: Srisakdi
Sukhumvit Set: Sukhumvit Set
Superclarendon: Superclarendon
Symbol: Symbol
System Font: System Font
Tahoma: Tahoma
Tamil MN: Tamil MN
Tamil Sangam MN: Tamil Sangam MN
Telugu MN: Telugu MN
Telugu Sangam MN: Telugu Sangam MN
Thonburi: Thonburi
Times: Times
Times New Roman: Times New Roman
Tiro Bangla: Tiro Bangla
Tiro Devanagari Hindi: Tiro Devanagari Hindi
Tiro Devanagari Marathi: Tiro Devanagari Marathi
Tiro Devanagari Sanskrit: Tiro Devanagari Sanskrit
Tiro Gurmukhi: Tiro Gurmukhi
Tiro Kannada: Tiro Kannada
Tiro Tamil: Tiro Tamil
Tiro Telugu: Tiro Telugu
Toppan Bunkyu Gothic: Toppan Bunkyu Gothic
Toppan Bunkyu Midashi Gothic: Toppan Bunkyu Midashi Gothic
Toppan Bunkyu Midashi Mincho: Toppan Bunkyu Midashi Mincho
Toppan Bunkyu Mincho: Toppan Bunkyu Mincho
Trattatello: Trattatello
Trebuchet MS: Trebuchet MS
Tsukushi A Round Gothic: Tsukushi A Round Gothic
Tsukushi B Round Gothic: Tsukushi B Round Gothic
Verdana: Verdana
Waseem: Waseem
Wawati SC: Wawati SC
Wawati TC: Wawati TC
Webdings: Webdings
Wingdings: Wingdings
Wingdings 2: Wingdings 2
Wingdings 3: Wingdings 3
Xingkai SC: Xingkai SC
YuGothic: YuGothic
YuKyokasho Yoko: YuKyokasho Yoko
YuMincho: YuMincho
Yuanti SC: Yuanti SC
Yuppy SC: Yuppy SC
Yuppy TC: Yuppy TC
Zapf Dingbats: Zapf Dingbats
Zapfino: Zapfino
cmb10: cmb10
cmex10: cmex10
cmmi10: cmmi10
cmr10: cmr10
cmss10: cmss10
cmsy10: cmsy10
cmtt10: cmtt10
If you are writing your document in LaTeX, the cmXXXX fonts might be of interest to you, as they correspond to the fonts used in LaTeX documents. Here is an example:
cmfont = font_manager.FontProperties(fname=mpl.get_data_path() + '/fonts/ttf/cmr10.ttf')
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 12,
'axes.titlesize': 12,
'axes.labelsize': 12,
'axes.labelpad': 12,
'lines.linewidth': 1,
'lines.markersize': 10,
'xtick.labelsize' : 10,
'ytick.labelsize' : 10,
'xtick.top' : True,
'xtick.direction' : 'in',
'ytick.right' : True,
'ytick.direction' : 'in',
'font.family' : 'serif',
'font.serif' : cmfont.get_name(),
"axes.formatter.use_mathtext": True,
'text.usetex': True,
'mathtext.fontset' : 'cm'
})x=np.linspace(0,np.pi,100)plt.figure(figsize=get_size(6,5),dpi=150)
plt.plot(x,np.sin(x))
plt.xlabel(r"velocity $v$")
plt.ylabel(r"position $r$")
plt.show()
Preparing a Document
When creating a document (bachelor thesis, for example), it is useful to organize your data and texts skillfully to save work. Here is an example,
from directory_tree import DisplayTree
DisplayTree("Example")Example/
├── data/
│ └── Figure1/
│ ├── Figure1.html
│ └── Figure1.ipynb
├── Figures/
│ └── figure1.pdf
├── literature.bib
├── main.pdf
└── main.qmd