This page was generated from `/home/lectures/exp3/source/notebooks/L18_AMA/Metals.ipynb`_.
Metals¶
Metals have free charges, which modify the propagation of light. Their influence is large and gives metals their characteristic reflection and color. In this case, we have to include the free charge density
Drude Model¶
The model we would like to put forward is the Drude model. It considers the motion of a charge in the electromagnetic field of a wave. As compared to our previous attempts on bound electrons in atoms, there is no direct restoring force for the free charges in the metal. The equation of motion therefore looks as
Here, the coefficient
where
from which we obtain an expression for
with
which is called the plasma frequency. It is a characteristic for each metal, since the density of free charges in the metal enters the equation. It is located in the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Dielectric function¶
With our previous definition of the complex refractive index we may now analyze the result of the dielectric function in terms of the Drude model. Using
the dielectric function, which is the square of the refractive index, is given by
We can therefore relatex the real part
and the imaginary part
of the dielectric function
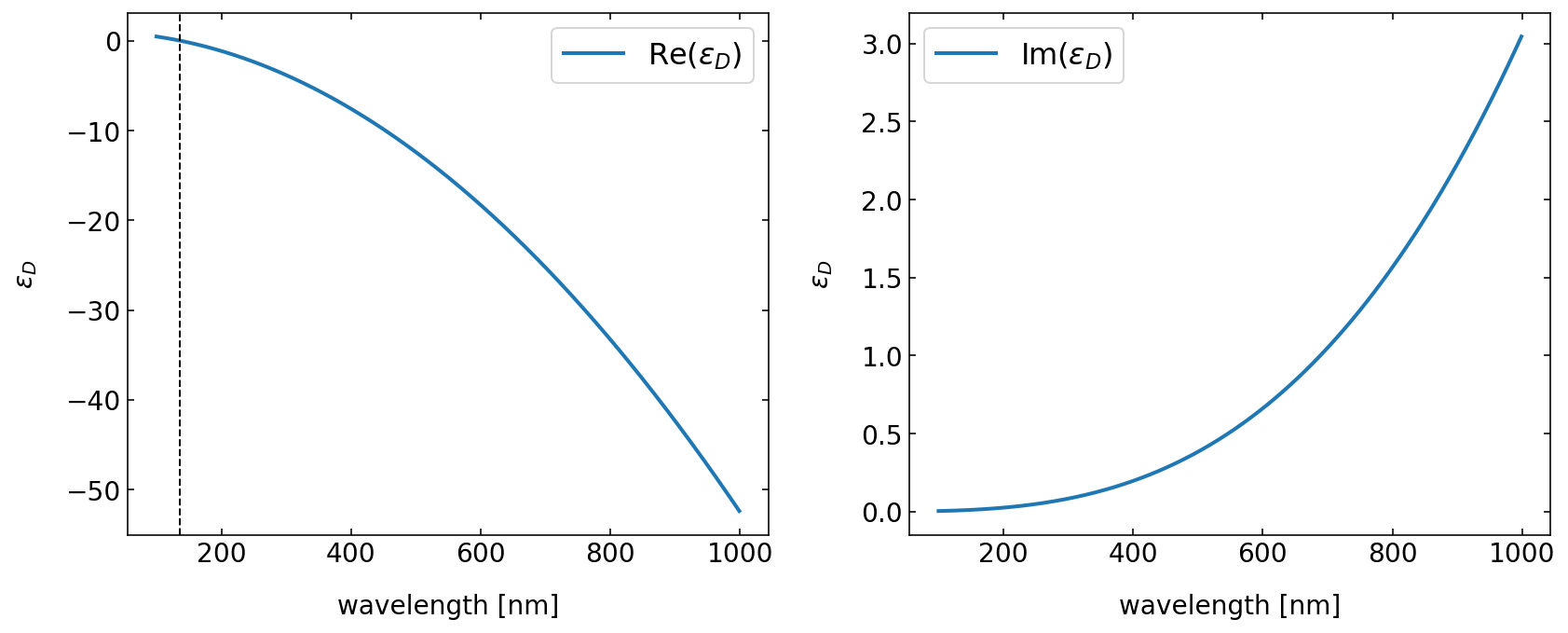
Fig.: Real (left) and imaginary part (right) of the dielectric function according to the Drude model. The dashed line in the left plot corresponds to the plasma frequency. The calculations are for Gold.
The figure above shows the dielectric function for Gold as determined from the parameters
Conductivity¶
As we calculate the position
where we explicity wrote the current density on the right side. Following this relation, the conductivity is obtained as
from the Drude model and we may express the real and imaginary parts of the dielectric function also in relation to the conductivity by
which readily tells us, that we obtain information about conductivity at high frequencies from optical measurements.
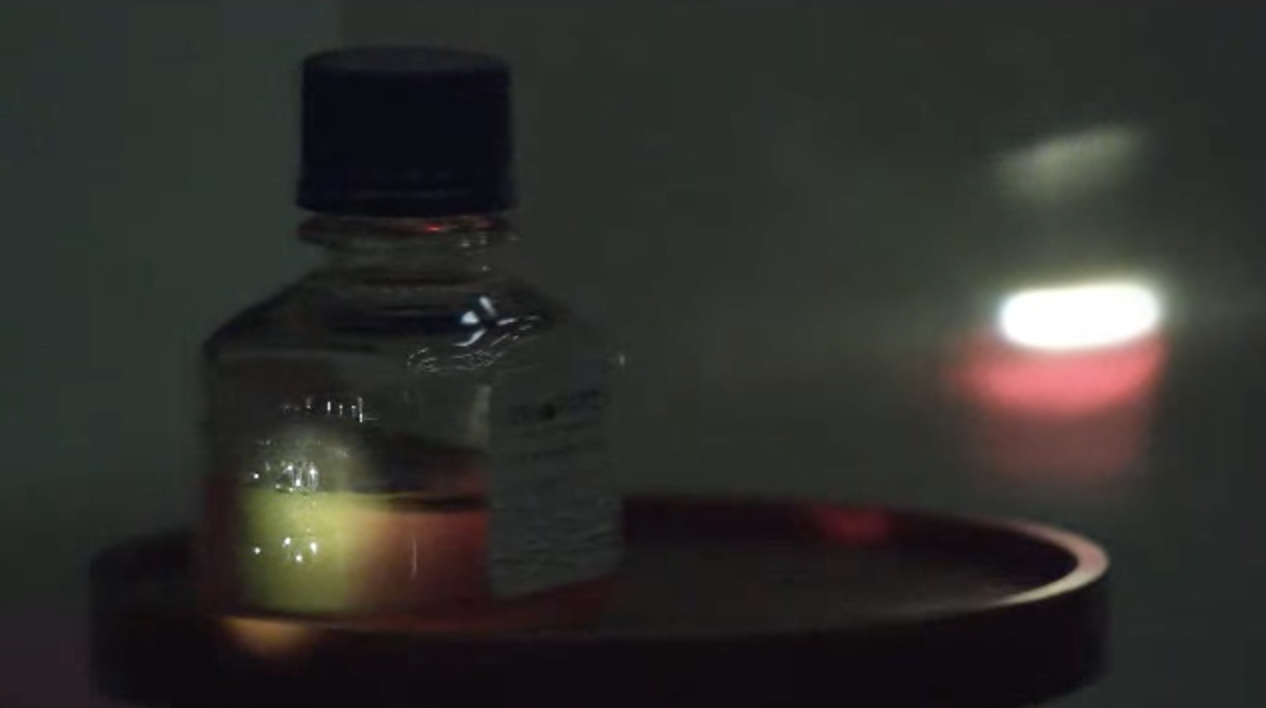

Fig.: Backscattering and transmission through a 65 nm gold nanoparticle solution. The backscattering is green due to the surface plasmon resonance of the conduction band electrons, while the transission is red, since the green light is removed by scattering.
